CoPIM: A Concurrency-aware PIM Workload Offloading Architecture for Graph Applications
Published in The 2021 IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Low Power Electronics and Design (ISLPED 2021), 2021
Liang Yan, Mingzhe Zhang, Rujia Wang, Xiaoming Chen, Xingqi Zou, Xiaoyang Lu, Yinhe Han, Xian-He Sun
Background
PIM architecture enables computation near memory, reducing the memory wall bottleneck prevalent in data-heavy applications. However, determining the optimal workload to offload to PIM, especially under high concurrency, is essential for maximizing efficiency.
Design
CoPIM introduces a Pure Miss Cycle Rate metric to guide workload partitioning based on concurrency and cache miss patterns. This metric helps CoPIM identify critical portions of graph workloads that can be offloaded to PIM units without compromising CPU performance. CoPIM’s architecture also includes an Instruction Management Unit (IMU) to manage loop-based offloading dynamically, improving the responsiveness of offloading decisions.
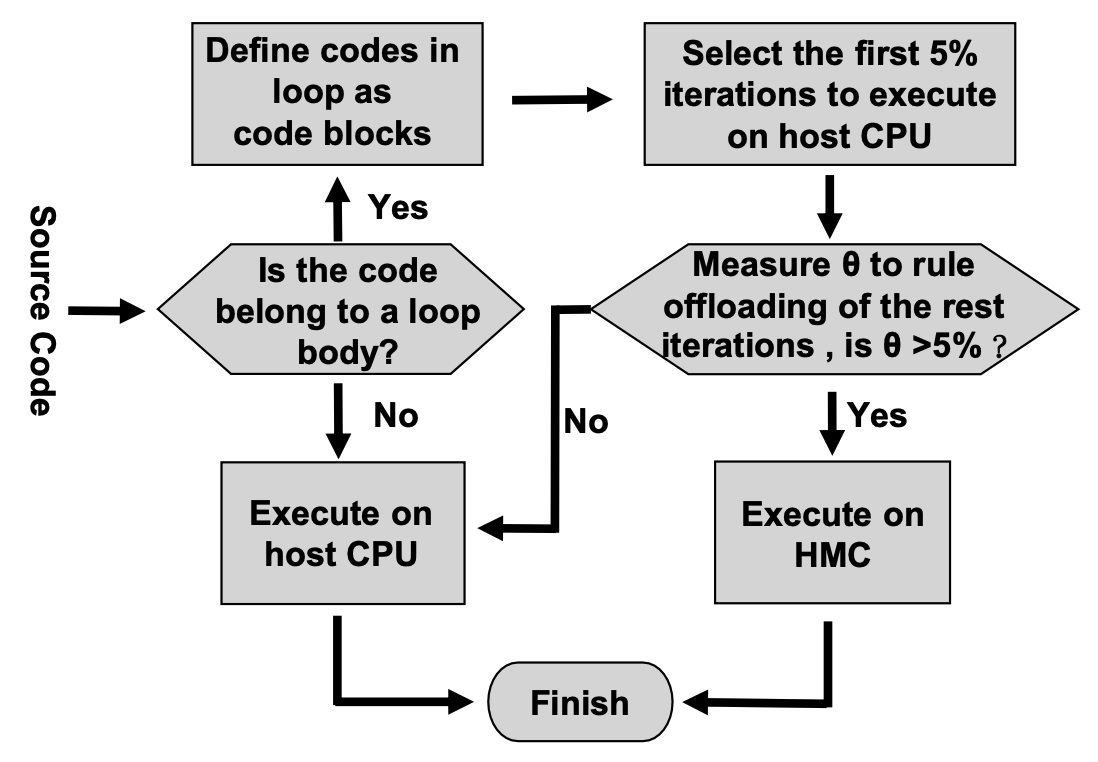
CoPIM workflow for selecting offloading targets
Key Features
- Pure Miss Cycle Rate (θ): Measures concurrency and cache utilization to determine suitable workloads for PIM execution.
- Dynamic Workload Partitioning: Adapts offloading decisions in real-time, focusing on high-impact code segments for enhanced system efficiency.
Results
CoPIM outperforms PEI and GraphPIM with a 19.5% and 11.4% speedup, respectively, demonstrating significant energy efficiency improvements due to reduced offloading overhead.
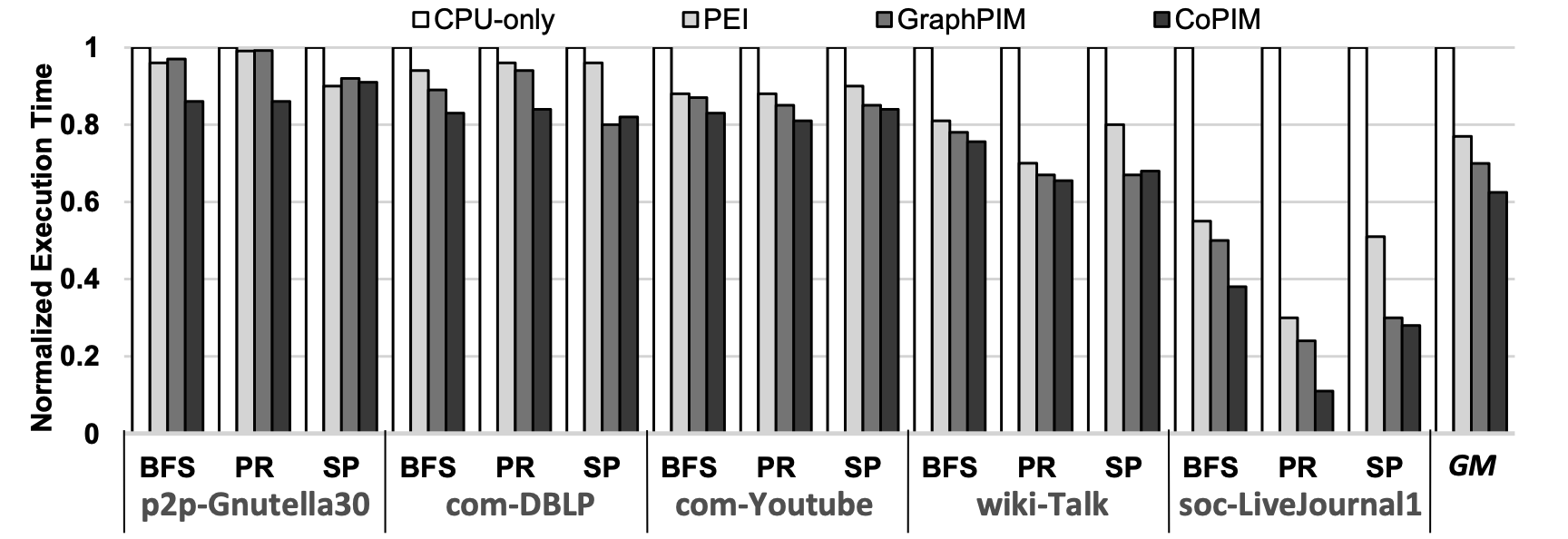
Performance comparison of state-of-the-art frameworks
Conclusion
CoPIM showcases that concurrency-aware workload partitioning in PIM can optimize graph application performance, especially in data-intensive environments, establishing a new standard for workload offloading strategies in PIM architectures.
