Premier: A Concurrency-Aware Pseudo-Partitioning Framework for Shared Last-Level Cache
Published in The 2021 IEEE 39th International Conference on Computer Design (ICCD 2021), 2021
Xiaoyang Lu, Rujia Wang, Xian-He Sun
Background
As multi-core processors handle increasingly complex applications, shared last-level caches (LLCs) experience contention, leading to performance degradation. Cache partitioning can mitigate this by controlling cache allocations per core, but it often overlooks concurrency.
Design
Premier leverages Pure Misses Per Kilo Instructions (PMPKI), a concurrency-aware metric that optimizes cache partitioning decisions by assessing the real cost of cache misses under concurrent access. By focusing on pure misses rather than total misses, Premier improves both performance and fairness across workloads.
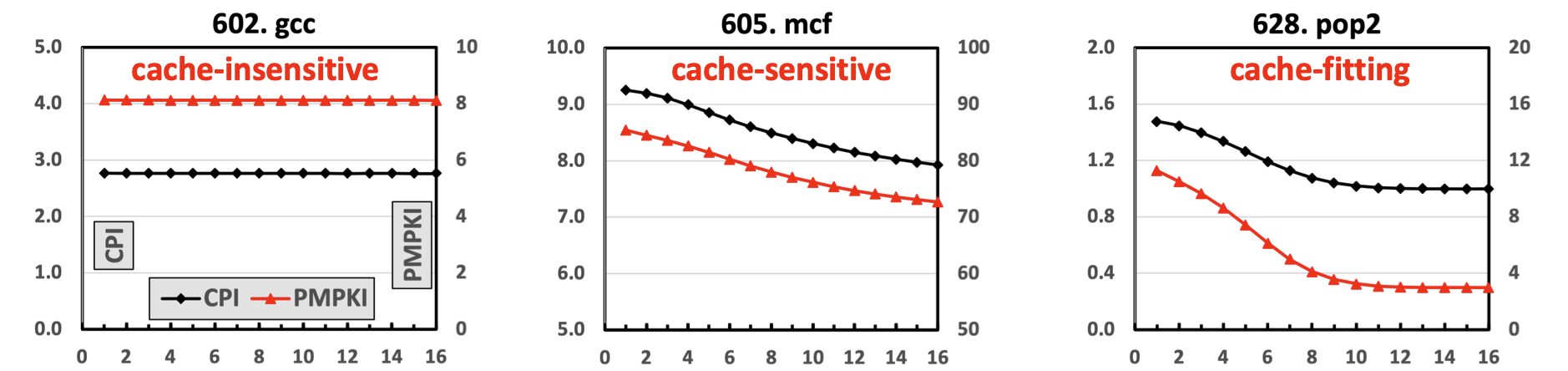
PMPKI and CPI (Cycle Per Instruction) for SPEC CPU 2017 benchmarks as the cache size is varied. The x-axis represents the number of ways allocated from a 16-way L3 shared cache.
Key Features
- Pure Misses Per Kilo Instructions (PMPKI): Assesses cache miss impact in concurrent access scenarios, providing an effective indicator for partitioning decisions.

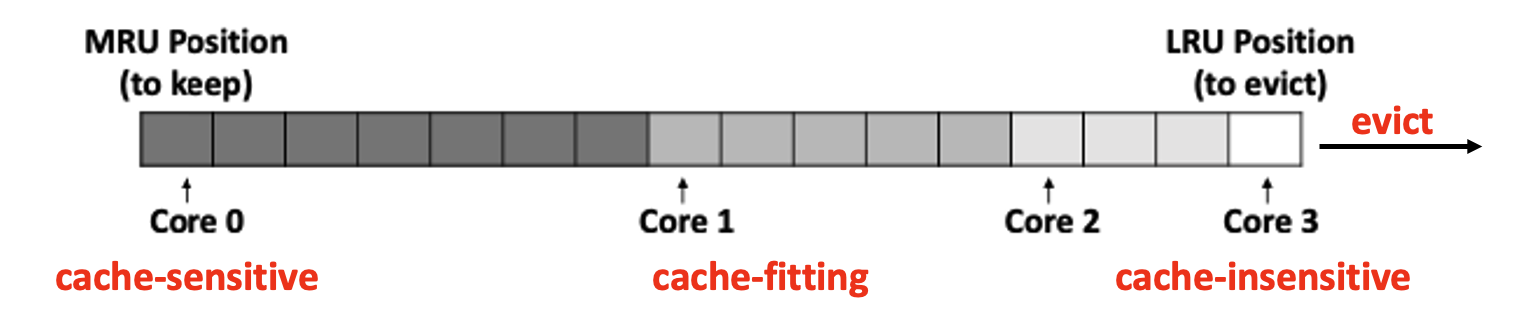
- Dynamic Cache Allocation: Using PMPKI curves, Premier adapts cache allocation in real-time, balancing between performance and fairness for each application in multi-core setups.
Results
Premier outperforms traditional partitioning schemes, achieving a 15.45% performance improvement and a 10.91% fairness increase in 8-core systems, demonstrating its strength in managing shared LLC resources effectively.
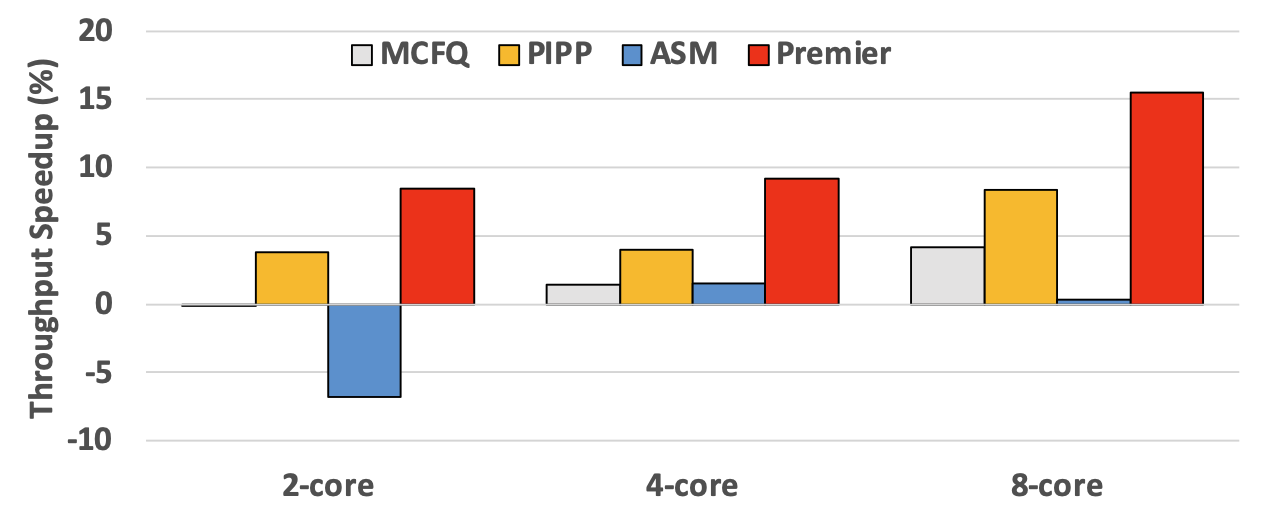
Throughput with varying core count
Conclusion
Premier’s concurrency-aware approach to cache partitioning highlights the importance of pure misses in optimizing cache efficiency, especially in scenarios with high core counts and shared resources.
