COSMOS: RL-Enhanced Locality-Aware Counter Cache Optimization for Secure Memory
Published in 2025 58th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture (MICRO 2025), 2025
Haoran Geng, Xiaoyang Lu, Yuezhi Che, Ziang Tian, Dazhao Cheng, Xian-He Sun, Michael Niemier, X. Sharon Hu
Background
Secure memory systems such as Intel SGX and AMD SEV use AES-CTR encryption with Merkle Trees (MT) to protect data confidentiality and integrity. While secure, these systems incur high performance penalties due to counter (CTR) cache misses. Each CTR miss triggers multiple DRAM and MT node accesses, dramatically increasing memory traffic and latency, especially for irregular workloads like graph processing.
Traditional solutions (e.g., MorphCtr, EMCC) improve cacheability or relocate CTR caches earlier in the hierarchy, but still struggle with irregular access patterns and introduce hardware complexity.
Design
COSMOS (Counter Optimized Secure Memory Operation Scheme) addresses these bottlenecks by leveraging reinforcement learning (RL) to make CTR cache management adaptive and locality-aware. It introduces two RL-based predictors:
- Data Location Predictor: Determines whether data after an L1 miss resides on-chip or off-chip. For predicted off-chip accesses, COSMOS speculatively accesses both data and its CTR earlier, reducing critical-path latency and populating the cache with hot CTRs.
- CTR Locality Predictor: Learns which CTRs exhibit good reuse locality, guiding the LCR-CTR (Locality-Centric CTR) cache to preferentially retain them and evict low-locality CTRs.
Together, these predictors form an RL-driven cache management framework that adapts online to workload dynamics with minimal hardware modifications.
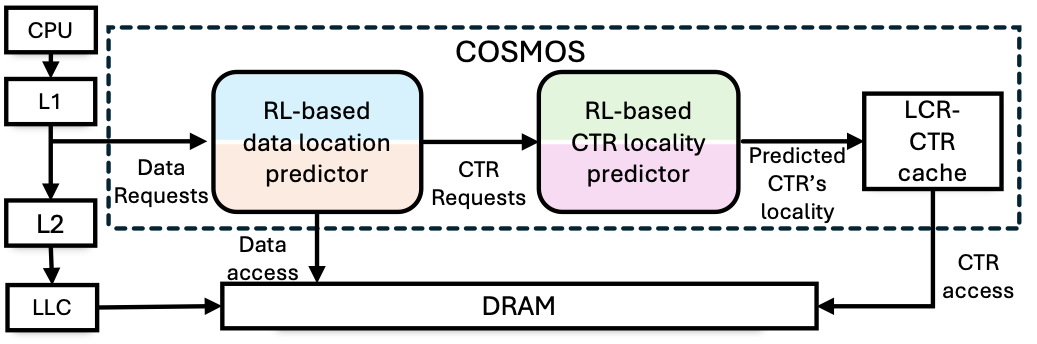
Overview of the COSMOS architecture with RL-based predictors and LCR-CTR cache
Key Features
- Dual RL Predictors
Data location predictor enables early CTR access immediately after L1 misses. - Locality-Centric CTR Cache (LCR-CTR)
Retains CTRs marked as high-locality for longer, evicting less critical ones. - Adaptive Online Learning
RL agents refine predictions continuously, eliminating the need for costly offline training. - Lightweight Hardware Overhead
Requires only 147KB additional storage (≈1.8% of an 8MB LLC).
Results
COSMOS demonstrates substantial performance gains over prior secure memory schemes:
- 25% improvement over MorphCtr on irregular workloads.
- 10% better performance than EMCC, while avoiding complex L2 controller modifications.
- Scalable: Maintains ~26% speedup in 8-core systems.
- Resilient: Provides modest gains (~3%) without harming performance in regular workloads.
Conclusion
COSMOS introduces an RL-enhanced, locality-aware optimization for secure memory systems. By integrating dual RL predictors with a locality-centric CTR cache, it reduces CTR cache miss rates and Secure Memory Access Time. The result is a practical, adaptive, and high-performance solution that significantly improves secure memory efficiency with minimal hardware cost.
